To select a diamond you must take into consideration some basic things.
The unique characteristics of a loose diamond are generally referred to the 5 C’s
Carat, Cut, Colour, Clarity and Certification
The weight of a diamond (carats) compared with all other characteristics can determine the rarity and furthermore the value of the diamond.
CARATS
The weight of a diamond is measured in carats.
1 carat = 0, 2 grams
1 carat is divided into 100 points.
Therefore a half carat diamond can be shown most usually as 50 points diamond or 0.50 carat.
As the carat of a diamond increases, so does the value, assuming that other characteristics (5 C’s) are the same.
CUT
Cut refers to the SHAPE of a diamond and the CUT CLASSIFICATION which reflects to the overall finish grade.
The most common diamond shapes are:
ROUND (70% of the whole diamond market has round shape)
PRINCESS
EMERALD
HEART
MARQUISE
TRILLION
OVAL
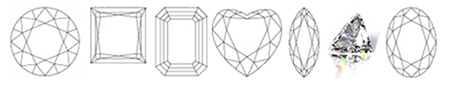
Round Princess Emerald Heart Marquise Trillion Oval
The cut classification of a diamond can vary from the ideal cut to poor.
The most popular cut classifications are:
VERY GOOD
GOOD
MEDIUM
POOR
COLOUR
An international colour grading scale is established to grade the colourless of a diamond.
Completely colourless diamonds are rare. Most of the diamonds, although they appear colourless, have a slight colour or shades that can be determined only under magnification and proper lighting conditions. Colour grades range from D to Z with D being the highest grade (exceptional white +) and S to Z being the bottom grades (tinted colour – yellow)
D = Exceptional white +
E = Exceptional white
F = Rare white +
G = Rare white
H = White
I & J = Slightly tinted white
K & L = Tinted white
M to R = Tinted colour (from scale M mildly hinds of colour is presented and approaching
scale R the tone of light yellow to yellow is vary
S to Z = Tinted colour – yellow
The very rare coloured fancy diamonds are exceptions to the above grading scale.
The natural coloured diamonds like blue, pink, green and orange can be found at very high prices. Natural bright yellow coloured diamonds can be found at the categories from X to Z at similar or even higher prices as category D.
CLARITY
Another international clarity grading scale is established to grade the flawless of a diamond.
Flawless or loupe-clean diamond is defined if after examination with a loupe 10X, under normal light conditions, has been found free of internal characteristics – inclusions.
So as the colourless, flawless diamonds are rare.
Clarity grading scale can be found as below:
LOUPE CLEAN or FL to IF = Flawless without any inclusions under 10X magnification.
VVS 1 to VVS 2 = Very very small inclusions, difficult to see under 10X magnification.
VS 1 to VS 2 = Very small inclusions which are invisible to the naked eye.
SI 1 to SI 2 = Small inclusions, easy to see with 10X magnification, difficult to see with naked
eye.
P1 to P3 or I1 to I3 = Medium to large inclusions, usually obvious to a gemmologist without
magnification.
CERTIFICATION
Extensive scientific testing and gemmological analysis can be done by an independent laboratory to evaluate and document in a written report all the above (carat, cut, colour and clarity).
In addition, some other important gemmological characteristics can be recorded on the certificate such as fluorescence, measurements, proportions and percentages of table and depth.
The most popular and acceptable certificates in Europe can be issued by the following authorities:
HRD - Diamond High Council, Antwerp, Belgium
EGL - European Gemmological Laboratory
GIA - Gemmological Institute of America
IGI - International Gemmological Institute